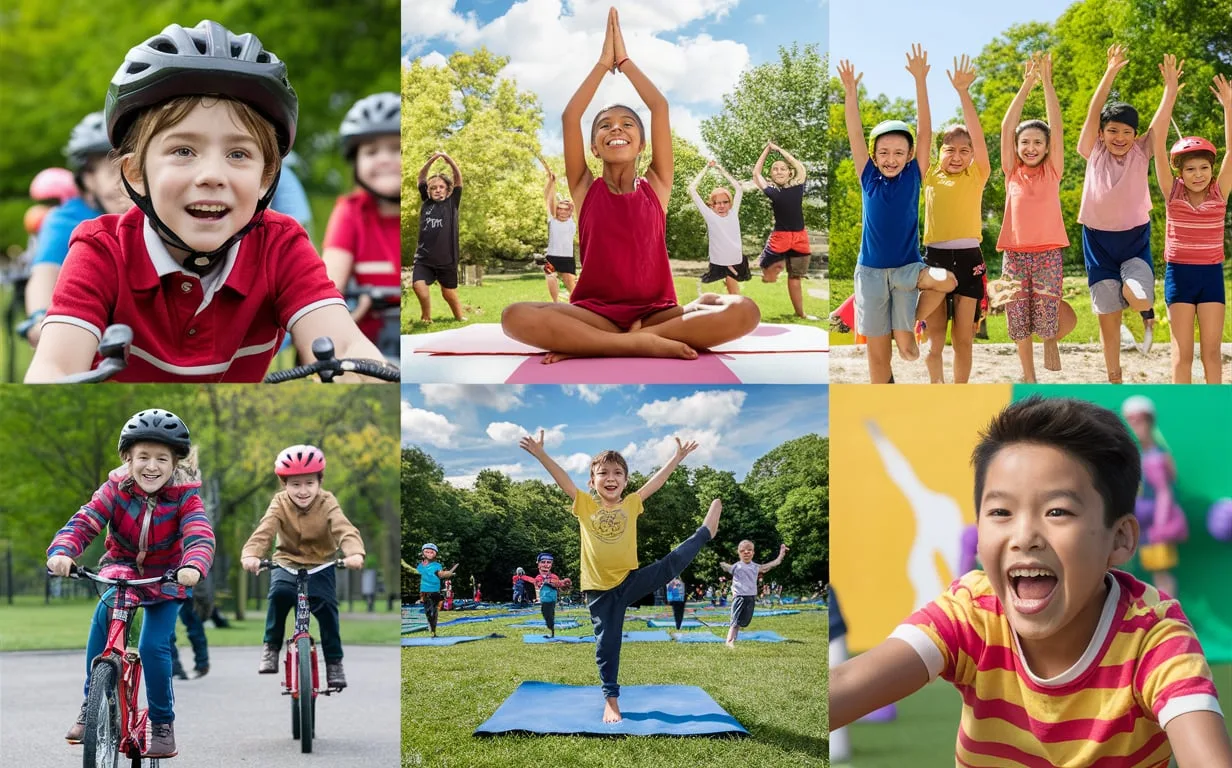
Physical activity is crucial for the healthy development of children, influencing everything from their physical health to their cognitive and emotional well-being. In an era where children are increasingly sedentary due to technology and screen time, promoting regular physical activity is more important than ever. Engaging in physical activities not only contributes to the growth and development of a child’s body but also fosters lifelong habits that encourage health, happiness, and well-being. This article explores the significant role physical activity plays in childhood health and offers practical ways to encourage children to stay active.
Benefits of Physical Activity for Children
- Physical Health: One of the most obvious benefits of physical activity is its positive impact on a child’s physical health. Regular exercise strengthens muscles and bones, improves cardiovascular health, and enhances flexibility and coordination. Activities like running, cycling, swimming, or even dancing build endurance and increase overall fitness. Children who are physically active are also less likely to develop chronic conditions such as obesity, heart disease, and type 2 diabetes. Exercise promotes a healthy metabolism, burns excess calories, and helps maintain a healthy weight.In fact, childhood obesity is a growing concern worldwide, and physical activity is one of the most effective ways to combat this issue. Regular movement not only helps children maintain a healthy weight but also builds a strong foundation for a lifetime of health-conscious behaviors.
- Cognitive Development: Physical activity plays an important role in a child’s brain development and cognitive function. Studies have shown that children who engage in regular physical exercise tend to perform better academically. Exercise increases blood flow to the brain, which improves concentration, memory, and overall mental clarity. Activities like running, swimming, or even playing sports also promote the development of key skills like problem-solving, decision-making, and multitasking.Additionally, physical activity has been shown to increase the production of endorphins, chemicals in the brain that promote feelings of happiness and reduce stress. This creates a positive feedback loop where physical activity helps children feel better emotionally, making them more engaged in their learning and social interactions.
- Social and Emotional Development: Physical activity offers numerous social benefits for children. Participating in team sports, group games, or even outdoor activities like hiking or playing at the park provides opportunities for children to interact with their peers, make friends, and develop social skills. These activities teach important values such as teamwork, cooperation, communication, and sportsmanship.Moreover, regular physical activity helps children develop self-confidence and self-esteem. As children master physical skills, they gain a sense of accomplishment and pride. Success in physical challenges can translate into increased resilience in other areas of life, fostering an emotional and mental outlook that encourages perseverance and determination.
- Mental Health and Well-Being: The benefits of physical activity extend beyond physical and cognitive development to include emotional health. Regular exercise is a powerful tool for combating anxiety, depression, and stress. Physical activity helps children release pent-up energy and emotions in a healthy way, reducing feelings of frustration or irritability. It can also serve as a positive outlet for dealing with life’s challenges.In an age where children and adolescents are increasingly exposed to stressors, such as academic pressure and social media influences, physical activity serves as an important coping mechanism. Exercise has been linked to improved mood, better sleep, and reduced symptoms of anxiety and depression. By encouraging physical activity, parents and caregivers provide children with a valuable strategy for managing emotions and building resilience.
Recommended Amount of Physical Activity
To reap the many benefits of physical activity, children need to engage in age-appropriate physical activities regularly. The World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend that:
- Children aged 3-5 years: Should engage in at least 3 hours of physical activity per day, including a mix of moderate to vigorous-intensity activities. This can include free play, running, climbing, or dancing.
- Children aged 6-17 years: Should engage in at least 1 hour of moderate to vigorous physical activity every day. This should include activities that strengthen muscles and bones, such as running, biking, swimming, or participating in sports like soccer or basketball.
Physical activity should be varied to keep children engaged and motivated. A mix of aerobic exercises, such as walking, running, or swimming, along with activities that improve strength, flexibility, and coordination, such as yoga or gymnastics, can provide a balanced and enjoyable fitness routine.
Encouraging Physical Activity in Children
Incorporating physical activity into a child’s daily routine doesn’t have to be complicated. Here are some ways to encourage children to stay active:
- Make it Fun: Choose activities that are enjoyable for your child. Whether it’s dancing, playing a sport, or simply running around in the park, making exercise fun ensures children are more likely to stick with it.
- Be a Role Model: Children often imitate their parents, so by engaging in physical activity yourself, you set a positive example. Go for family walks, bike rides, or participate in outdoor games together.
- Create an Active Environment: Limit screen time and encourage outdoor play. Set up a safe, engaging space where children can run, jump, and explore freely.
- Join in Group Activities: Involve your child in group activities such as team sports, hiking clubs, or community fitness events. These provide opportunities for children to socialize while staying active.
- Set Realistic Goals: Help children set achievable fitness goals, whether it’s walking a certain number of steps, learning a new sport, or completing a fun run. Celebrate their progress to keep them motivated.
Conclusion
Physical activity plays a vital role in childhood health by supporting physical, cognitive, emotional, and social development. Regular exercise strengthens the body, improves brain function, boosts mental health, and helps children develop important social skills. As children grow, establishing healthy physical activity habits can lay the foundation for a lifetime of well-being. Parents and caregivers can help foster these habits by creating a supportive environment that encourages movement, provides opportunities for fun activities, and sets a good example. With the right balance, physical activity can become a natural and enjoyable part of every child’s life, promoting their overall health and happiness.